Introduction
In the digital and marketing landscape, channels play a crucial role. They serve not only as mere transmission paths for data between different components such as RAM and peripheral devices but also encompass the functional modules that enable autonomous control and monitoring of input and output operations. In the following article, you will learn more about the different output channels.
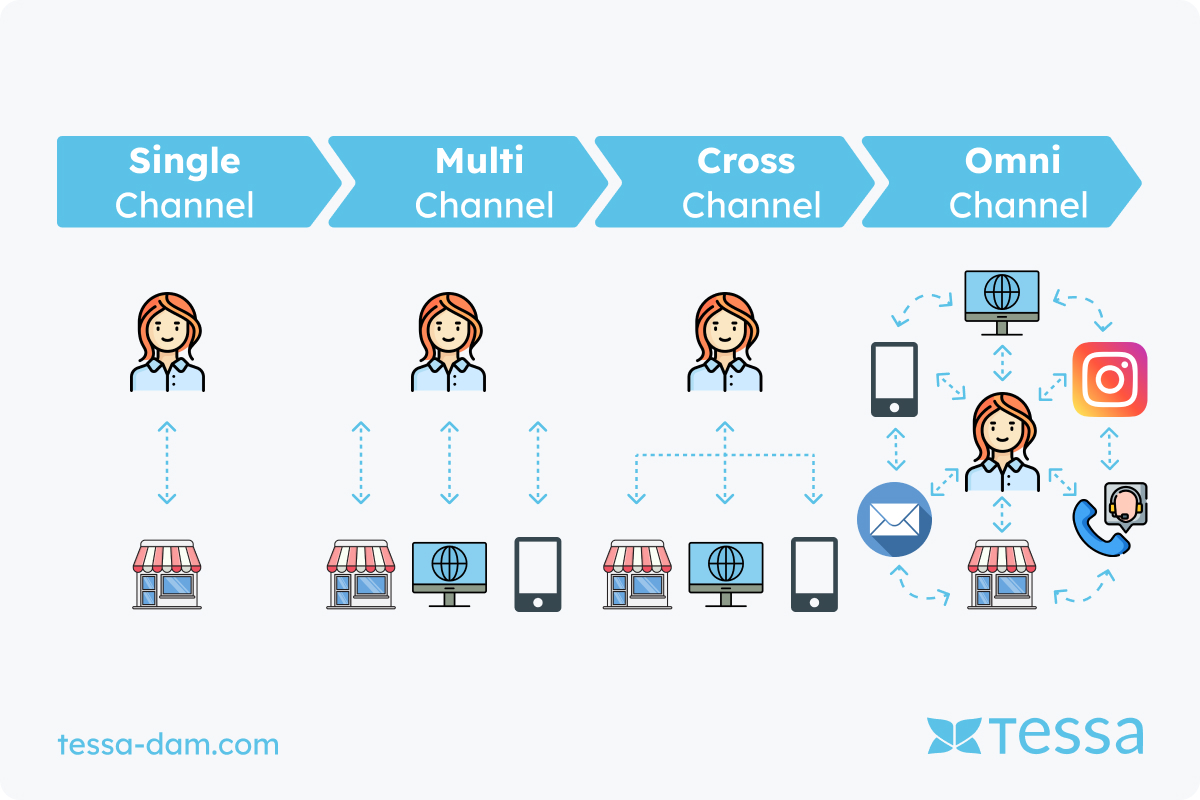
Single-Channel: Focus on one Path
The single-channel approach, also known as single-channel, describes the practice where a merchant exclusively distributes their products through a single distribution channel. This can be done, for example, through a dedicated online store or a physical store. In this model, the customer only has the option to process their purchases through this specific channel.
Multi-Channel Management: Coordination of various Pathser Wege
Multi-Channel Management refers to the coordinated use of various distribution channels by a company. This can include sales through physical stores, the use of field sales representatives, as well as operating a webshop. These channels are operated separately and independently of each other. Managing data for different channels can be done through a PIM system (Product Information Management), which provides a central database for product information.
Cross-Channel: Linking various Paths
Cross-Channel represents another level of channel integration. Here, the various distribution channels are linked together to provide customers with a seamless transition experience between channels. A typical example would be linking a print catalog with an online store via product codes or QR codes, allowing customers to easily switch between physical and digital shopping options. By using Cross-Channel strategies, companies can convey a consistent brand message across different channels and strengthen customer loyalty. Effective Cross-Channel management requires careful planning and integration of the various channels, as well as a comprehensive data strategy to ensure that all channels have access to current and consistent information.
Omnichannel: Integration of all Paths
The Omnichannel approach is characterized by the seamless integration of various distribution channels. Here, all channels work together to provide customers with a consistent and seamless experience. Unlike Multi-Channeling, the channels in Omnichannel are interconnected and communicate with each other to ensure a unified shopping experience. A PIM system also plays an important role here, as it ensures that all channels have access to the same current product information.
Conclusion
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Path
Overall, channels play a crucial role not only in data transmission but also in sales management. The choice between Single-Channel, Multi-Channel, Cross-Channel, and Omnichannel strategies depends on the individual needs of the company as well as the expectations and preferences of the customers.