Basics of Omnichannel Marketing
What is Omnichannel?
The term "Omnichannel" refers to a comprehensive and integrated marketing strategy where all of a company's available sales channels are seamlessly connected to provide customers with a consistent and smooth experience. Unlike traditional multichannel approaches, where different channels often operate independently, omnichannel marketing aims to synchronize all customer interactions and touchpoints across various channels. This means that a customer can, for example, research a product online, purchase it in-store, and then receive support through mobile applications without the quality of the customer experience or the brand message being compromised. A key aspect of omnichannel marketing is the central role of customer experience, which is optimized through a coherent and integrated approach across all channels.
The Role of Technology in Omnichannel
The successful implementation of omnichannel marketing heavily relies on the effective use of modern technologies. Data analysis, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and artificial intelligence play a key role here. These technologies allow companies to collect, analyze, and use comprehensive customer data in real time to deliver personalized and relevant content across multiple channels. A crucial aspect is the integration of online and offline channels, enabling the company to create a unified and consistent customer experience. This integration requires not only technical solutions but also organizational adjustments to ensure that all departments and touchpoints within the company work harmoniously together. Technology acts as an enabler, making the complex requirements of omnichannel marketing achievable and laying the foundation for a successful strategy.
Omnichannel Marketing Goals
What is an Example of an Omnichannel Goal?
A key goal of omnichannel marketing is to improve customer satisfaction by providing a consistent and seamless experience across all contact points. This means that customers, whether interacting with a brand online, in-store, or via mobile applications, always experience a consistently high level of service quality and a unified brand message. A concrete example of an omnichannel goal could be increasing customer retention by providing personalized offers and relevant content across different channels. By synchronizing communication channels and leveraging customer data, the company can take targeted actions to better understand and meet individual customer needs. Another common goal is to increase revenue by guiding customers smoothly through an optimized customer journey from the first contact to the purchase decision.
Measuring the Success of Omnichannel Goals
To assess the success of omnichannel marketing strategies, it is necessary to define specific key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitor them regularly. Key KPIs in omnichannel marketing include Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), which measures the long-term value of a customer to the company, and the Net Promoter Score (NPS), which provides insights into customer satisfaction and the likelihood of customers recommending the brand. Other relevant metrics are the conversion rate, which measures how many potential customers ultimately become buyers, and the cross-channel retention rate, which shows how effectively the company can retain customers across multiple channels. Monitoring these KPIs allows the company to evaluate the success of its omnichannel efforts, identify weaknesses, and continuously make improvements to ensure that the set omnichannel goals are not only achieved but also maintained in the long term.
Developing an Omnichannel Strategy
What is an Omnichannel Strategy?
An omnichannel strategy is a comprehensive approach that aims to integrate all available sales channels and customer touchpoints of a company to ensure a seamless and coherent customer experience. Unlike traditional marketing strategies that often view individual channels in isolation, an omnichannel strategy focuses on the continuous connection of these channels. The goal is to provide the customer with a consistent and personalized experience, regardless of the channel through which they interact with the brand. This requires not only technological integration but also strategic alignment of all marketing and sales teams to ensure that the brand message and service are consistent across all platforms.
Components of a Successful Omnichannel Strategy
A successful omnichannel strategy is based on several key components:
-
Consistent brand messaging: The foundation of an omnichannel strategy is a unified and consistent brand message communicated across all channels. This builds trust and recognition with the customer and ensures that the brand is perceived clearly and coherently in every interaction.
-
Personalization and relevance: Another crucial component is the ability to deliver personalized and relevant content across all channels. By leveraging customer data and analytical tools, the company can offer targeted recommendations and offers that meet individual customer needs and preferences. This increases the likelihood of positive interactions with the brand and ultimately leads to a purchase decision.
-
Integration of e-commerce, social media, and physical stores: To create a truly seamless experience, all sales channels – including e-commerce platforms, social media, physical stores, and mobile applications – must be effectively integrated. This means that the customer can switch between channels without losing information or context. For example, a customer researching a product online should be able to access it seamlessly in-store and make the purchase there.
Challenges in Implementation
Implementing an omnichannel strategy involves various challenges, both technical and organizational:
-
Data silos and organizational barriers: In many companies, customer data is stored in separate systems (data silos), making it difficult to integrate and create a comprehensive view of the customer. A successful omnichannel strategy requires overcoming these silos through the use of integrated technologies and cross-departmental collaboration.
-
Adapting to changing customer needs: Customer expectations and needs are constantly changing, especially in today's digitally-driven world. Companies must be agile enough to continuously adapt their omnichannel strategy to these changes. This can be done, for example, through regular customer feedback analysis and testing new approaches.
-
Technological challenges: The technical integration of different channels, real-time data collection and analysis, and ensuring data security are other challenges to consider when implementing an omnichannel strategy. Companies must ensure that their technology platforms are scalable, flexible, and secure to meet the demands of omnichannel marketing.
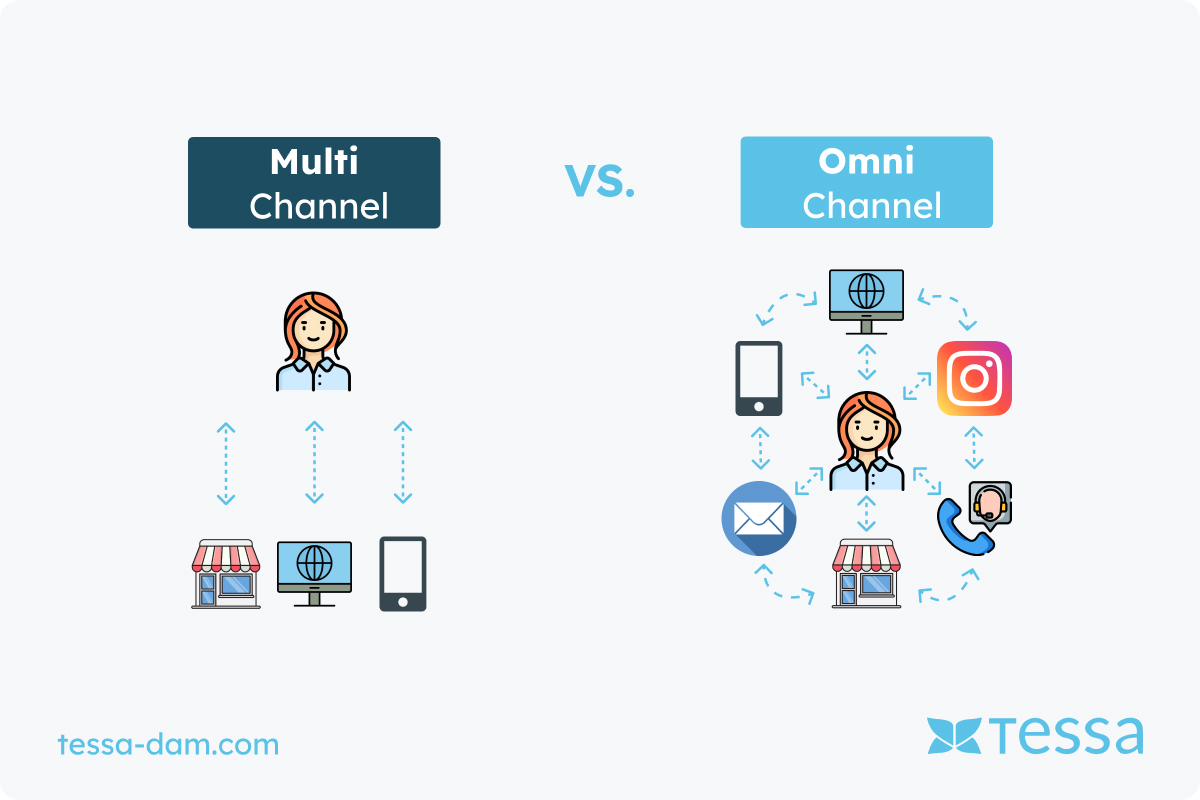
The Difference Between Multichannel and Omnichannel
The difference between multichannel and omnichannel primarily lies in how companies connect their sales channels and manage customer interactions. In multichannel marketing, companies use several channels, such as online stores, physical shops, social media, and mobile apps, to offer their products or services. However, these channels operate independently without deeper integration. Each channel functions on its own, requiring the customer to switch between them, often encountering different information and experiences on each one.
In contrast, omnichannel marketing aims to seamlessly integrate all these channels, providing customers with a consistent and unified experience. The focus is on customer interactions, allowing them to, for instance, start product research online, continue it via an app, and complete the purchase in-store without any loss of information or communication discrepancies. All channels work together as part of a cohesive system, enabling a much smoother and more coherent customer journey.
A key difference between the two approaches is the customer experience. While multichannel offers many contact points, it requires the customer to use the channels separately, which can lead to a fragmented brand experience. For example, a customer may place a product in their online shopping cart but have trouble accessing this information when they later visit a physical store. Omnichannel, on the other hand, ensures that all channels work in sync, with information flowing seamlessly. This allows the customer to effortlessly switch between channels, while the company tracks their interactions in the background to deliver a personalized experience.
From a technological and organizational standpoint, the omnichannel approach requires more integration than multichannel. In multichannel marketing, channels can operate separately on different systems, often resulting in fragmented customer data. In omnichannel marketing, centralized CRM systems and databases are used to provide a comprehensive view of the customer. This enables companies to not only offer a smooth customer experience but also deliver personalized offers and content in real time.
Omnichannel Campaigns
What Are Omnichannel Campaigns?
Omnichannel campaigns are marketing initiatives specifically designed to deliver a unified and consistent message across all relevant channels, creating a seamless customer experience. Unlike traditional campaigns, which are often channel-specific, omnichannel campaigns integrate various communication channels – such as email, social media, mobile apps, physical stores, and more – linking them together. The goal is to accompany the customer along their entire customer journey and provide personalized and coherent content at every touchpoint. Customer data is centrally collected and analyzed to understand behavior, preferences, and needs, allowing the brand to meet the customer exactly where they are in their journey with the company.
Planning and Executing Omnichannel Campaigns
The successful execution of omnichannel campaigns requires careful planning and close coordination between various departments within the company. Key steps include:
-
Identifying and segmenting target audiences: The first step in planning an omnichannel campaign is to accurately identify and segment target audiences. The customer base is analyzed based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchasing behavior, or preferences, to ensure that the campaign is tailored to the specific needs and interests of the target groups.
-
Selecting and integrating appropriate channels: Based on the target audience analysis, the channels that are most relevant to the respective audience are selected. These can include both online channels such as email and social media, as well as offline channels such as direct mailings or in-store promotions. It is crucial that these channels are not viewed in isolation but are integrated within the campaign to ensure a consistent message.
-
Timing and relevance: A key success factor for omnichannel campaigns is the right timing. Messages must be delivered to the customer at the right time and place. The relevance of the content plays a decisive role: only if the content is tailored to the individual needs and context of the customer can it be effective.
Conclusion
Omnichannel marketing for customer proximity
Omnichannel marketing offers companies the opportunity to create a seamless and consistent customer experience by integrating and synchronizing all sales channels. By leveraging technology and customer data, personalized and relevant content can be delivered across all touchpoints, leading to higher conversion rates and long-term business success. Given the ever-changing customer needs and technological developments, omnichannel marketing remains a critical factor for companies to remain competitive in the digital age.